Concept
- Problems
- Solutions
Developing new tools...
To fill the gap between new genomic conservation approaches and DNA sequencing technologies, we are developing tools to automatically process samples into the field and accelerate biodiversity identification!

RaPId
(Rapid Plant IDentification)

CoWaS
(Continuous Water Sampler)

JAWS
(Just Another Water Sampler)
Developing new tools...
To fill the gap between new genomic conservation approaches and DNA sequencing technologies, we are developing tools to automatically process samples into the field and accelerate biodiversity identification.

CoWaS
(Continuous Water Sampler)
enabling the use of DNA analysis...
Biologist and botanists have enlarged their toolbox thanks to the latest biotechnology advances.
The cost reduction of next-generation sequencing is popularizing access to new genomic techniques in conservation. The standardization of barcoding coupled with biodiversity databases such as BOLD has increased the speed of species identification.

DNA barcoding for plant
The use of DNA barcoding has deeply impacted taxonomy over the last decade, evolving from a species detection method to a tool for the identification and discovery of new species.
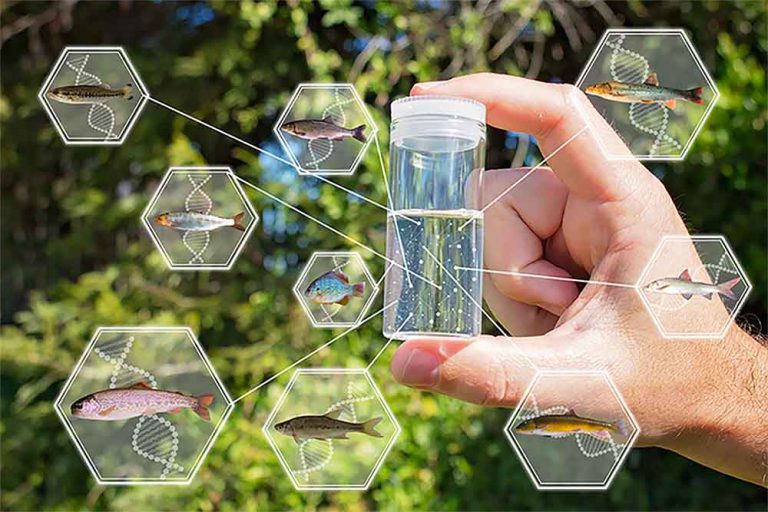

Environmental DNA for water samples
The emerging approaches such as Environmental DNA and Environmental DNA metabarcoding are unleashing and empowering new applications in biomonitoring, invasion biology, conservation biology and ecology.
to speed up data collection...
The developed devices will enhance biodiversity monitoring by providing a new way to acquire data on ecosystems and biodiversity with the creation of a database integrating all the data collected.
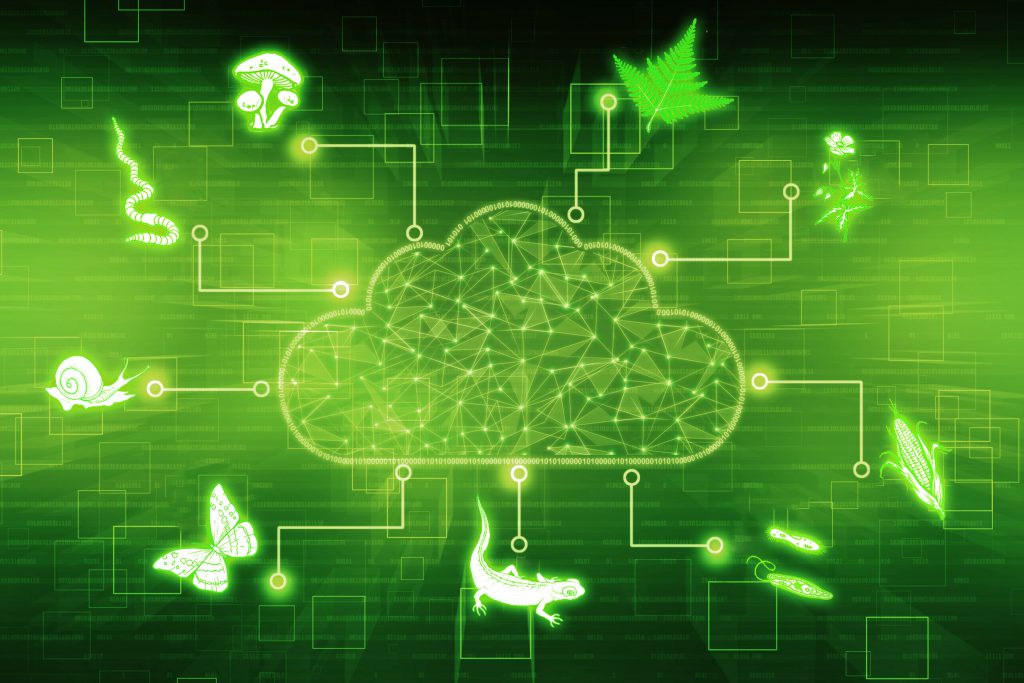

Database
GenoRobotics’ main impact is the creation of a biodiversity database interfacing with existing systems such as the Barcode Of Life or GenBank .
Interfacing tools
This wouldn’t be possible without the interface between the tool and the computer, to allow fast and reliable transfers.
Consensus sequence
The data collected, the genome, is huge. To identify species and provide further data analysis, only specific parts are seeked and stored in the database.
...to tackle the biodiversity crisis
Today we face the 6th mass extinction in our planet’s history
Biodiversity preservation has become a major challenge of the XXIst century
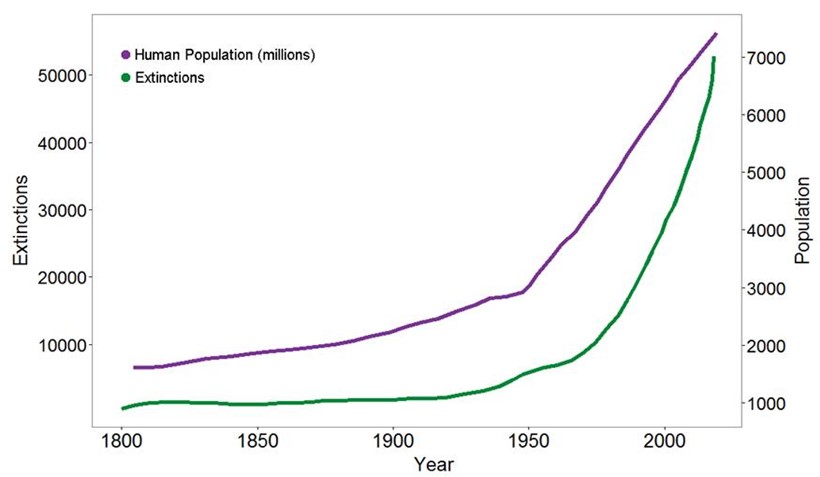
The Anthropocene
How can Earth’s biodiversity and humans coexist in a world entering a new epoch: the Anthropocene
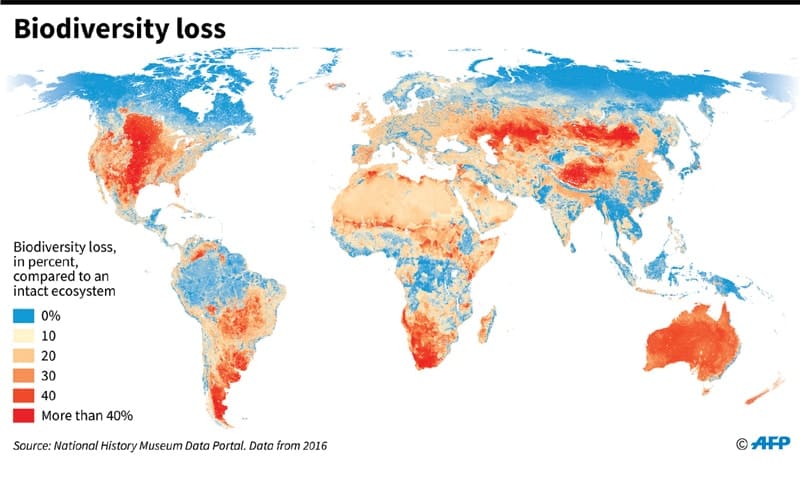
Repartition of biodiversity loss
On all continents, ecological disasters occur more frequently and biodiversity is the main casualty: the vertebrate population decreased by 60% in 40 years.
